Your cart is currently empty!
2015 Membership Survey Results are here!
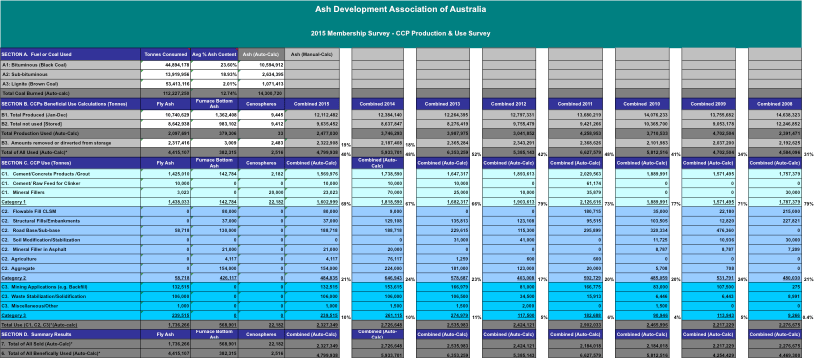
Annual members and non-members were surveyed for CCPs generated, stored and sold during the reported period, which provides results for the calendar year; January to December 2015. Information provided by members and non-members was collated, compared with other data sources for verification purposes and then aggregated into national data set.
The beneficial use of coal combustion products (CCPs) during 2015 resulted in 4.8 million tonnes or 40% being effectively utilised and this is due to partly a function of the continued demand within the supply chains for cement and concrete. This demand for fine and coarse aggregate use in structural/civil applications continues to be closely tied to consumption or growth in future development of infrastructure in both urban and regional Australia – estimated to be in excess of 160 million tonnes annually.
Key results;
Approximately 12.1Mt (megaton) of CCPs were produced within Australasia. On a per capita basis, this equates to about 500 kg/person.
- Some 4.8 Mt or 40% of CCPs produced have beeneffectively utilisedin various value-added products or to some beneficial end over the period. On a per capita basis, this equates to about 202 kg/person recycled or reused.
- Approximately 1.6 Mt or 69% of effectively utilised coal ashwas used in high value-added applications such as cementitious binders, concrete manufacture or mineral fillers.
- About 0.50 Mt or 21% of effectively utilised coal ash was used in non-cementitious applications such as flowable fills, structural fills, road bases, coarse/fine aggregates and mine site remediation.
- Some 2.3 Mt or 19% was used in projects offering some beneficial use (e.g. onsite remediation, local haul roads etc.). These uses typically generate no economic return, that is, cost avoidance or recovery only.
- Surplus CCPs of 9.6 Mt are typically placed into onsite storage ponds awaiting some future opportunity for economic reuse.
- More than 45 Mt of CCPs [fly ash] have been used in cementitious applications or concrete manufacture from 1975 to 2015 [39 years].
The survey results include all generators, marketers and users for the total production and resulting sales by each end use. In summary, the recovery and reuse of CCPs provides positive and significant environmental impacts, including resource conservation and in this case, the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions from the processing of virgin resources, resulting in the reduction of greenhouse gases. The survey results can be seen below.